 Vue2的extend与手动挂载$mount
Vue2的extend与手动挂载$mount
因为用 Webpack 基本都是前端路由的,它的 html 里一般都只有一个根节点 <div id="app"></div>,其余都是通过 JavaScript 完成,也就是许多的 Vue.js 组件(每个页面也是一个组件)其内的所有内容都是在#app 内渲染的。当我们需要异步,或是在非#app 下的位置进行渲染时,Vue.extend 和 vm.$mount 语法就派上用场了。
vue.extend 的作用,就是基于 vue 构造器,创建一个子类,作为一个函数,配合$mount,让组件渲染并挂载到任意的节点上。
// 创建构造器
const anyComponent = Vue.extend({
template: "<div>{{name}}是帅哥</div>", // 模版语法
props: ["girlfriend"],
data() {
// data, 像组件一样使用函数的形式
return {
name: "cd",
};
},
});
// 传递data参数(调用$mount前,此时还未完成渲染),new之后的component已经是一个标准的vue组件实例了
const component = new anyComponent({
girlfriend: 10000000000000000000000,
});
// 并挂载到#cd-boss元素上
component.$mount("#cd-boss");
// 或是这样的快速挂载的方法
new anyComponent({ el: "#cd-boss" });
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
除了用 extend 之外,还可以通过创建一个新得 vue 实例来渲染出一个 vue 文件:
import Vue from "vue";
import Message from "./xxx.vue";
const props = {}; // 这里可以传入一些组件的 props 选项
const Instance = new Vue({
render(h) {
return h(Message, {
props: props,
});
},
});
const component = Instance.$mount();
document.body.appendChild(component.$el);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# $mount 的源码 (opens new window)
通过查阅$mount的源码,更加清楚的认识$mount 的作用是什么。
/*把原本不带编译的$mount方法保存下来,在最后会调用。*/
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
/*挂载组件,带模板编译*/
Vue.prototype.$mount = function(
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el);
/* 这里很简单,首先去判断是否有挂载的根节点,且根节点是一个dom节点 */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" &&
warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
);
return this;
}
// 这里的$options其实就是在组件内书写的data\props等对象
const options = this.$options;
// 处理template模版,template及其他形式的模版最终都会转换成render函数的形式,
// 但如果有render函数优先采用render,不会去编译template
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template;
// template存在的时候取template,不存在的时候取el的outerHTML
if (template) {
/*当template是字符串的时候*/
if (typeof template === "string") {
if (template.charAt(0) === "#") {
template = idToTemplate(template);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && !template) {
warn(
`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,
this
);
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
/*当template为DOM节点的时候*/
template = template.innerHTML;
} else {
/*报错*/
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
warn("invalid template option:" + template, this);
}
return this;
}
} else if (el) {
/*获取element的outerHTML*/
template = getOuterHTML(el);
}
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && config.performance && mark) {
mark("compile");
}
/*
* 将template编译成render函数,这里会有render以及staticRenderFns两个返回,
* 这是vue的编译时优化,static静态不需要在VNode更新时进行patch,优化性能
*/
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(
template,
{
shouldDecodeNewlines,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
},
this
);
options.render = render;
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && config.performance && mark) {
mark("compile end");
measure(`${this._name} compile`, "compile", "compile end");
}
}
}
/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*/
/*调用const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount保存下来的不带编译的mount*/
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
通过 mount 代码我们可以看到,在 mount 的过程中,如果 render 函数不存在(render 函数存在会优先使用 render)会将 template 进行 compileToFunctions 得到 render 以及 staticRenderFns。render function 在运行后会返回 VNode 节点,供页面的渲染以及在 update 的时候 patch。 接下来看看这个 compileToFunctions 是做什么的。
/*作为缓存,防止每次都重新编译*/
const functionCompileCache: {
[key: string]: CompiledFunctionResult,
} = Object.create(null);
/*带缓存的编译器,同时staticRenderFns以及render函数会被转换成Funtion对象*/
function compileToFunctions(
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions,
vm?: Component
): CompiledFunctionResult {
options = options || {};
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
// detect possible CSP restriction
try {
new Function("return 1");
} catch (e) {
if (e.toString().match(/unsafe-eval|CSP/)) {
warn(
"It seems you are using the standalone build of Vue.js in an " +
"environment with Content Security Policy that prohibits unsafe-eval. " +
"The template compiler cannot work in this environment. Consider " +
"relaxing the policy to allow unsafe-eval or pre-compiling your " +
"templates into render functions."
);
}
}
}
/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*/
// check cache
// 在进入compileToFunctions以后,会先检查缓存中是否有已经编译好的结果,
// 如果有结果则直接从缓存中读取。这样做防止每次同样的模板都要进行重复的编译工作。
const key = options.delimiters
? String(options.delimiters) + template
: template;
if (functionCompileCache[key]) {
return functionCompileCache[key];
}
// compile
/*编译*/
const compiled = compile(template, options);
// check compilation errors/tips
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
if (compiled.errors && compiled.errors.length) {
warn(
`Error compiling template:\n\n${template}\n\n` +
compiled.errors.map((e) => `- ${e}`).join("\n") +
"\n",
vm
);
}
if (compiled.tips && compiled.tips.length) {
compiled.tips.forEach((msg) => tip(msg, vm));
}
}
// turn code into functions
const res = {};
const fnGenErrors = [];
/*将render转换成Funtion对象*/
res.render = makeFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors);
/*将staticRenderFns全部转化成Funtion对象 */
const l = compiled.staticRenderFns.length;
res.staticRenderFns = new Array(l);
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
res.staticRenderFns[i] = makeFunction(
compiled.staticRenderFns[i],
fnGenErrors
);
}
// check function generation errors.
// this should only happen if there is a bug in the compiler itself.
// mostly for codegen development use
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
if ((!compiled.errors || !compiled.errors.length) && fnGenErrors.length) {
warn(
`Failed to generate render function:\n\n` +
fnGenErrors
.map(({ err, code }) => `${err.toString()} in\n\n${code}\n`)
.join("\n"),
vm
);
}
}
/*存放在缓存中,以免每次都重新编译*/
return (functionCompileCache[key] = res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
compile 主要做了两件事,一件是合并 option(前面说的将平台自有的 option 与传入的 option 进行合并),另一件是 baseCompile,进行模板 template 的编译。
/*编译,将模板template编译成AST树、render函数以及staticRenderFns函数*/
function compile(template: string, options?: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {
const finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions);
const errors = [];
const tips = [];
finalOptions.warn = (msg, tip) => {
(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg);
};
/*做下面这些merge的目的因为不同平台可以提供自己本身平台的一个baseOptions,内部封装了平台自己的实现,然后把共同的部分抽离开来放在这层compiler中,所以在这里需要merge一下*/
if (options) {
// merge custom modules
/*合并modules*/
if (options.modules) {
finalOptions.modules = (baseOptions.modules || []).concat(
options.modules
);
}
// merge custom directives
if (options.directives) {
/*合并directives*/
finalOptions.directives = extend(
Object.create(baseOptions.directives),
options.directives
);
}
// copy other options
for (const key in options) {
/*合并其余的options,modules与directives已经在上面做了特殊处理了*/
if (key !== "modules" && key !== "directives") {
finalOptions[key] = options[key];
}
}
}
/*基础模板编译,得到编译结果*/
const compiled = baseCompile(template, finalOptions);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
errors.push.apply(errors, detectErrors(compiled.ast));
}
compiled.errors = errors;
compiled.tips = tips;
return compiled;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
来看一下 baseCompile.baseCompile 首先会将模板 template 进行 parse 得到一个 AST 语法树,再通过 optimize 做一些优化,最后通过 generate 得到 render 以及 staticRenderFns。
function baseCompile(
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
/*parse解析得到ast树*/
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options);
/*
将AST树进行优化
优化的目标:生成模板AST树,检测不需要进行DOM改变的静态子树。
一旦检测到这些静态树,我们就能做以下这些事情:
1.把它们变成常数,这样我们就再也不需要每次重新渲染时创建新的节点了。
2.在patch的过程中直接跳过。
*/
optimize(ast, options);
/*根据ast树生成所需的code(内部包含render与staticRenderFns)*/
const code = generate(ast, options);
return {
ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns,
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
compile 编译可以分成 parse、optimize 与 generate 三个阶段
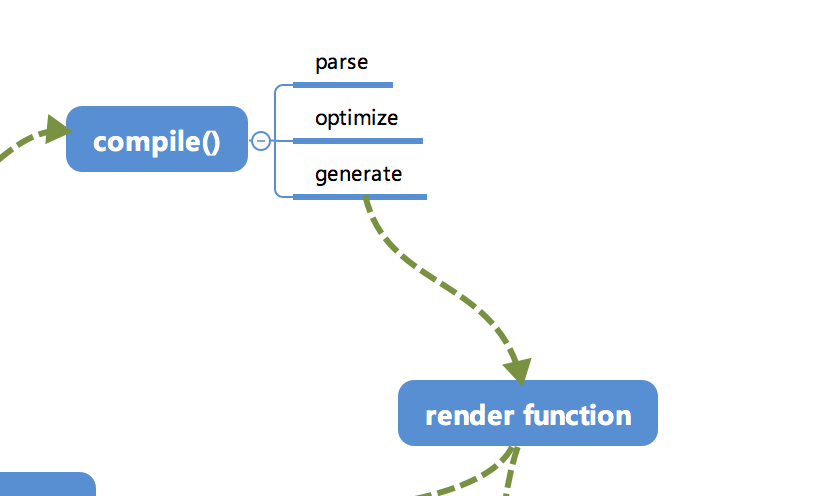
- parse parse 的源码可以参见 github.com/answershuto… (opens new window)。 parse 会用正则等方式解析 template 模板中的指令、class、style 等数据,形成 AST 语法树。
- optimize optimize 的主要作用是标记 static 静态节点,这是 Vue 在编译过程中的一处优化,后面当 update 更新界面时,会有一个 patch 的过程,diff 算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了 patch 的性能。
- generate generate 是将 AST 语法树转化成 render funtion 字符串的过程,得到结果是 render 的字符串以及 staticRenderFns 字符串。